According to recent study human skin cells emit slow electric pulses after being injured. These signals likely play a role in coordinating with injured cells for wound healing. Those electrical pulses travel a short distance, potentially alerting neighboring cells to prepare for the repair process after got injured.
According to researchers those electric spikes are a surprise because only nerve cells were thought to communicate this way. These signals move at a snail’s pace compared to nerve impulses and can be detected at least 500 micrometers away about the distance of 40 cells.
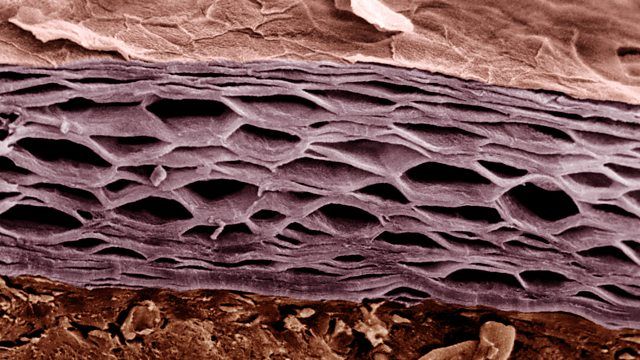
Cell biologist Min Zhao of the University of California, ‘’says they didn’t know that skin cells can send of electric pulses the way nerve cells do.’’
Bioengineer Sun-Min Yu and engineering scientist Steve Granick from of the University of Massachusetts made an arrangement to record this phenomenon. They grew human skin cells or dog kidney cells on electrode-lined chips. Both are epithelial cells, a cell type that forms barriers such as skin and mucous membranes, and also lines organs and body cavities. After blasting some cells with lasers, they measured tiny shifts in electrical activity.
Bioengineers found that the pulses generated by both the skin and kidney cells are partly driven by the flow of calcium ions and have about the same voltage as a nerve cell zap. But the spikes move at a crawl compared to nerve cell signals. Whereas nerve cell impulses last just milliseconds, epithelial cells take one to two seconds to spit out their electrical messages.
During the experiments they found wounded cells sent pulses for more than five hours. This is possibly alerting neighbors to squeeze out damaged cells and to start replicating to repair the wound. Such slow, long-lasting signaling makes sense. While nerve cells drive split-second reactions, epithelial cells heal wounds over days to weeks.



1 comment
Gyet Rover
I didn’t know this before , fantastic article by The Mirror Science, love read?such articles and some about space science